Where viruses and bacteria cause cancer
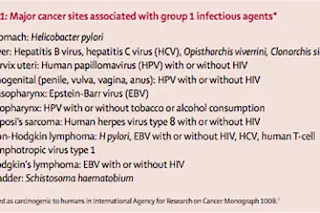
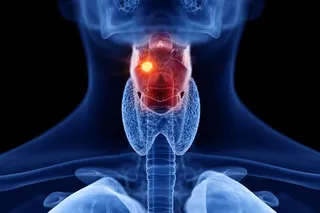
Strictly speaking, cancer is not contagious. But a fair number of cancers are clearly caused by viral or bacterial infections: lymphomas can be triggered by the Epstein-Barr virus, which also causes mononucleosis. Liver cancers can be caused by Hepatitis B and C. Cervical cancers can be caused by human papillomavirus, the major reason behind the development of a vaccine against it. For some of these cancers, nearly 100% of the cases have an infectious link---when researchers check to see if a virus or bacterium is working in the tumor or has left signs of its presence in a patient's blood, the answer is nearly always yes.
A new paper in The Lancet takes a look at the very best data on the prevalence of infection-caused cancers and comes up with some striking numbers. Overall, they estimate that 16% of cancer cases worldwide in 2008 ...