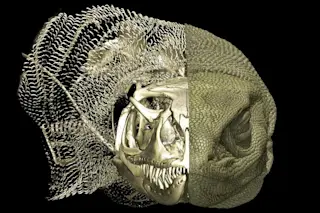
For a few months of the year, the Alaskan Arctic becomes flooded with birds. From shorebirds to waterfowl, these avians arrive in the spring to breed, nest, and raise their young, and to take advantage of the ample plants and prey (invertebrates and other animals) that thrive in Alaska’s short summers. They do it today, and they did it around 73 million years ago, too.
Documenting the earliest evidence ever discovered of birds breeding and nesting in the Arctic, a new study in Science describes a collection of avian fossils and fossil fragments from around 73 million years ago. The collection comprises dozens of bones and teeth from adult and baby birds, and it shows that avians similar to modern shorebirds and waterfowl reproduced in the Arctic in the Cretaceous period, when dinosaurs still dominated the Alaskan terrain.
“Birds have existed for 150 million years,” said Lauren Wilson, a study ...