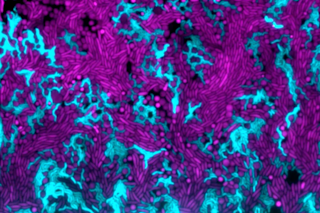
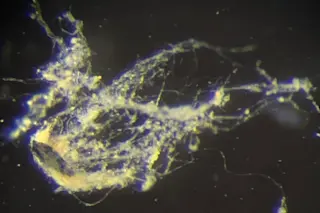
From the bubbling hot springs of Yellowstone National Park, researchers from Montana State University (MSU) have analyzed three thermophilic microbes, revealing how they may have adapted in a low-oxygen environment and evolved to live today.
After over two decades of research, the new study published in Nature Communications, highlights three microbes collected from two different hot springs within Yellowstone National Park.
With the new information gathered, researchers are hoping it can shed light on the way life evolved before the Great Oxidation Event occurred 2.4 million years ago. Prior to the event, Earth’s atmosphere contained about 2 percent oxygen. Afterward, it jumped to 20 percent.
Read More: Magma Beneath Yellowstone Appears to be on the Move
Thriving in Oxygen
Conch Spring and Octopus Spring were selected for microbe extraction because of their geochemical similarities, according to researchers Bill Inskeep, a professor in the Department of Land Resources and Environmental Sciences at MSU, and Mensur Dlakic, an associate professor in the Department of Microbiology and Cell Biology at MSU.
The study points out that Conch Spring has higher amounts of sulfide and oxygen compared to Octopus Spring. This difference helps the researchers compare the microbes with both high and low oxygen levels. The three microbes extracted from the springs were all thermophilic, meaning they thrived in high temperatures — each spring was about 190 degrees Fahrenheit.
“When oxygen started to increase in the environment, these thermophiles were likely important in the origin of microbial life,” said Inskeep, in a press release. “There was an evolution of organisms that utilized oxygen. Octopus has more oxygen and sure enough, there's more aerobic organisms there. These environments have different casts of characters.”
Studying Microbes
The research team analyzed the microbes Aquificota (Thermocrinis), Pyropristinus (Caldipriscus), and Thermoproteota (Pyrobaculum), which are all found within streamers that live in rapid water currents. Streamers may look like green, stringy algae that attach to rocks and other things within the spring. And when the water flows, they appear to wiggle.
The results showed how the thermophilic microbes grew and adapted in a more oxygen-rich environment. To get the results, the researchers looked at respiratory genes in the microbes from each spring and compared them. They found that the genes of the low-oxygen microbes from Conch Spring were more active. The microbes in the more oxygenated Octopus Spring were expressing genes that were more adapted to high oxygen levels.
“It would be very difficult to reproduce this kind of an experiment in the laboratory; imagine trying to [create] hot-water streams with just the right amounts of oxygen and sulfide,” Inskeep said in a press release. “And that’s what's so nice about studying these environments. We can make these observations in the exact geochemical conditions that these organisms need to thrive.”
What This Tells Us About Ourselves
While the average person may not think much of the microbes that dwell in the thermal pools of Yellowstone National Park, understanding them is another piece of the puzzle when it comes to understanding ourselves and how we have evolved.
“It may seem counterintuitive to understand complex life by studying something that's simple, but that's really how it has to start,” Dlakic said in a press release. “You have to think back to understand where we are today.”
Read More: Parasites May Create Wolf Pack Leaders in Yellowstone
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed studies and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors review for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources used below for this article: