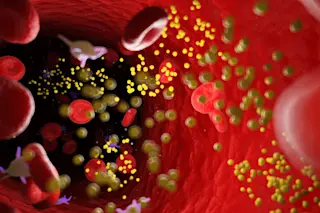
When C. Michael Gibson of Boston saw his doctor in the spring of 2023, the blood test results were confusing. His cholesterol levels were decent — he was already taking statins to keep the “bad” cholesterol low — but the arteries delivering blood to his heart were nonetheless crammed with dangerous plaque. “It didn’t make sense,” says Gibson, himself a cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
So Gibson asked his physician to check his blood for a specific kind of cholesterol called lipoprotein(a). And there was the explanation: He had more than double the normal amount of that cholesterol. Gibson turned out to be one of the unlucky people who has inherited a predisposition toward high lipoprotein(a) levels; he suspects that his grandfather, who died of a heart attack at age 45, had it too.
About one in five people have this unfortunate heritage, and there’s nothing they can ...