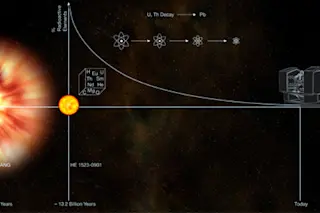
THE STUDY “Discovery of HE 1523-0901, a Strongly r-Process-Enhanced Metal-Poor Star With Detected Uranium,” by Anna Frebel et al., The Astrophysical Journal, May 10, 2007.
THE MOTIVE How do you determine the age of an ancient star? For distant galaxies, astronomers measure redshift—the stretching of light that indicates how fast the stars are receding and therefore how old they are relative to the age of the universe. But this doesn’t work for an ancient star nearby. So Anna Frebel of the McDonald Observatory at the University of Texas at Austin looked for chemical clues. She reckoned that a rare form of old “metal poor” star, one with one-thousandth the iron content of our own young sun, carries an internal clock, one composed of the radioactive elements uranium and thorium. Because these metals decay at a steady rate, an astute observer can extrapolate backward and pinpoint the star’s moment of birth. ...