When it comes to the human brain, even the simplest of acts can be counter-intuitive and deceptively complicated. For example, try stretching your arm. Nerves in the limb send messages back to your brain, but the subjective experience you have of stretching isn't due to these signals. The feeling that you willed your arm into motion, and the realisation that you moved it at all, are both the result of an area at the back of your brain called the posterior parietal cortex. This region helped to produce the intention to move, and predicted what the movement would feel like, all before you twitched a single muscle. Michel Desmurget and a team of French neuroscientists arrived at this conclusion by stimulating the brains of seven people with electrodes, while they underwent brain surgery under local anaesthetic. When Desmurget stimulated the parietal cortex, the patients felt a strong desire to move their arms, hands, feet or lips, although they never actually did. Stronger currents cast a powerful illusion, convincing the patients that they had actually moved, even though recordings of electrical activity in their muscles said otherwise. But when Desmurget stimulated a different region - the premotor cortex - he found the opposite effect. The patients moved their hands, arms or mouths without realising it. One of them flexed his left wrist, fingers and elbow and rotated his forearm, but was completely unaware of it. When his surgeons asked if he felt anything, he said no. Higher currents evoked stronger movements, but still the patients remained blissfully unaware that their limbs and lips were budging. These contrasting responses tell us two important things. Firstly, they show that our feelings of free will originate (at least partially) in the parietal cortex. It's the activity of these neurons that creates a sense that we initiate actions of our own accord. Secondly, they show that the sense of moving doesn't depend very much on actually doing so - it depends on calculations that are made in the parietal cortex, long before the action itself begins.
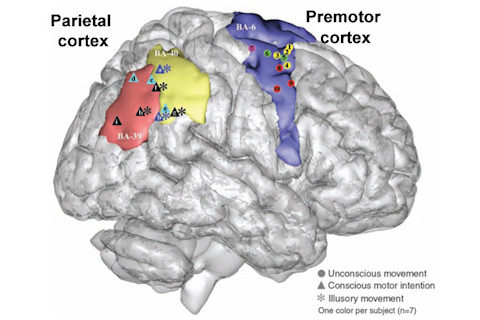
The seven patients in Desmurget's study were brain cancer patients, who were having their tumours removed. All of them gave consent to have their brains stimulated as part of the operations, something that's often done beforehand to check that everything's working and minimise the risk of major complications after the surgery. Stimulating the brain with electrodes in this way gets around a major problem with studying the idea of "free will" in a laboratory setting. It allows scientists like Desmurget to carefully control their experiments, delivering a very precise input and watching the result. The only alternative would be to give volunteers the outline of a task and get them to choose what action to make, when to make it or whether to make it at all. Another neuroscientist, Patrick Haggard, describes these experiments as "unsatisfactory, even paradoxical", the equivalent of instructing people to "have free will now!" Electrodes help to bypass that problem, and this isn't the first time that scientists have used them to the subjective side of movements. In 1991, Itzhak Fried
found that delivering an electric jolt
to a person's supplementary motor area (SMA) produced a strong urge to move. But unlike the desires experienced by Desmurget's patients, these urges felt strong and irrepressible, like they went beyond the patients' own will. With enough current to the SMA, Fried could trigger actual movements. Desmurget, on the other hand, could only ever produce the illusion of movement by focusing on the parietal cortex. And his patients' descriptions of their experiences made it very clear that they were feeling some sort of internal intention to move, rather than feeling compelled by an external force. Without any prompting from the researchers, they all described their feelings with words such as "will", "desire" or "wanting to". One of the patients said, "I felt a desire to lick my lips", after a low burst of current. With more stimulation, he said "I moved my mouth. I talked. What did I say?" These results are a good fit with those of previous studies. Research on monkeys suggests that the posterior parietal cortex contains a sort of "map of intentions", where different areas are dedicated to planning different groups of movements - looking, grasping, reaching, and so on. And in humans, people with parietal cortex damage
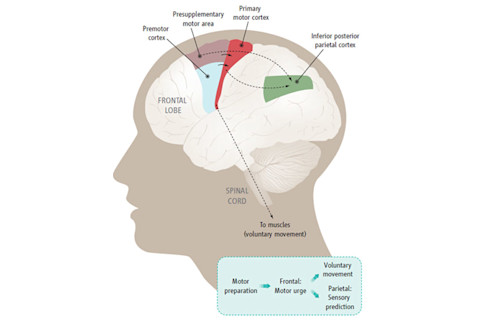
aren't aware of their intention to move. They can tell when they start moving, but not when they actually decided to do so. To Haggard, the SMA and the parietal cortex are two sides of the same coin. All the voluntary actions we do, from kicking a ball to opening a door, eventually pass through the primary motor cortex, the final staging ground where electrical thoughts are converted into muscular deed. This area receives inputs from two others - the premotor cortex, which governs movements that respond to something in the outside world, and the SMA, which is involved in actions that we make of our own accord. The SMA prepares commands for the actions we undertake. But it also communicates with the parietal cortex, which predicts what it would feel like to carry out those actions and create a sense of ownership over our own movements. Dualist philosophers like Descartes believed that the mind and consciousness exist outside the physical world, producing our actions by interacting with the physical meat of our brains. The idea has become commonplace, but it's challenged by neuroscientific studies like this one, which show that the conscious intention to move emerges from electrical activity in neurons, tangible objects that are all too real.
Reference: Desmurget, M., Reilly, K., Richard, N., Szathmari, A., Mottolese, C., & Sirigu, A. (2009). Movement Intention After Parietal Cortex Stimulation in Humans Science, 324 (5928), 811-813 DOI: 10.1126/science.1169896
Haggard, P. (2009). The Sources of Human Volition Science, 324 (5928), 731-733 DOI: 10.1126/science.1173827
More on consciousness: