Superbugs are pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that present serious threats in hospitals, exposing vulnerable patients to higher risks of infections and even death. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 2.8 million infections and 35,000 deaths annually are caused by microbe strains that have developed resistance to multiple drugs — one of the most significant global public health threats of this century.
Unfortunately, hospitals, where the most vulnerable patients are concentrated, also serve as breeding grounds for these superbugs, fostering pathogens like the well-known MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). This strain can cause serious bloodstream infections or pneumonia.
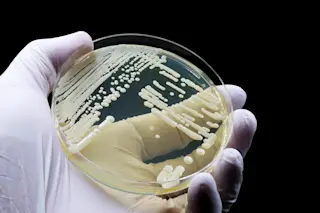
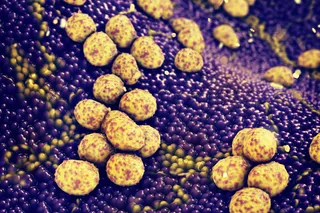
A relatively new and dangerous fungal pathogen, Candida auris, is also on the rise, prompting researchers to quantify these fungal infections and study how they manifest in patients. Their research, which included clinical cultures of C. auris collected between April 1, 2019, and December 31, 2023, was published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
The Danger of Candida auris Symptoms
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has classified C. auris as an "urgent antimicrobial resistance threat" for hospitals, following its first appearance in the U.S. in 2016. Discovered in Japan in 2009, the pathogen has spread worldwide, with health professionals fighting to contain it.
C. auris is closely related to C. albicans, a common cause of candidiasis, including fungal infections like thrush and vaginal yeast infections. These infections tend to take hold in people with weak immune systems, such as the elderly, infants, and those with immune deficiencies.
However, C. auris can cause more invasive forms of candidiasis that can spread into the bloodstream, central nervous system, and other internal organs — posing a more significant threat to health. The challenge with treating this pathogen is its ability to be misidentified as other, less harmful types of candida, and its multidrug resistance. Many common antimicrobial drugs are ineffective against superbugs, partly due to the overuse of antibiotics in healthcare settings.
Read More: Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: What They Are and How Scientists Are Combating Them
C. auris Cases Are Rising
A study focused on the health care system in Miami, Florida, highlights a troubling rise in C. auris infections, from just 5 cases in 2019 to 115 in 2023. Most infections were found in the bloodstream, but there has also been an increase in cases involving cerebrospinal fluid (the liquid surrounding the brain and spinal cord), as well as soft tissue and bone infections.
The fungus primarily spreads through medical equipment such as catheters, as well as breathing and feeding tubes. The CDC has issued a comprehensive list of recommendations to curb the spread of C. auris, which includes strict cleaning protocols for surfaces and devices, and using single-patient rooms when possible.
Additionally, all C. auris samples from the study showed resistance to fluconazole, a commonly used antifungal drug for treating serious fungal and yeast infections. Aside from its resistance to regular medical treatment, C. auris also shows resilience against common cleaning products and disinfectants.
Low Risk to the General Public
In 2023, there were already concerns about C. auris, with warnings about its spread across half of the U.S. states, indicating that authorities have been monitoring the issue for some time.
Although C. auris can lead to severe or fatal illnesses, at present it doesn’t pose much risk to the general public. Most healthy individuals are unlikely to contract the infection since they aren’t as exposed to C. auris, and their immune systems can typically fight it off. However, for people who are already ill and hospitalized, the growing threat is very real.
In terms of preventing the spread of C. auris, isolation and contact precautions are critical. According to the researchers in a press release, "Our findings suggest that early identification of patients colonized with C. auris and the prompt deployment of infection prevention strategies can potentially reduce the incidence of bloodstream infections."
This article is not offering medical advice and should be used for informational purposes only.
Read More: Hospital-Acquired Infections Are Rising: Here's How To Protect Yourself
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed studies and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors review for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources used below for this article:
American Journal of Infection Control: Changing trends in the sources and volumes of clinical cultures with Candida auris at an integrated health system in Miami, Florida, United States, 2019-2023
Centers for Disease Control: Antimicrobial Resistance Facts and Stats
Centers for Disease Control: Infection Control Guidance: Candida auris
Molecules: Multidrug Resistance (MDR): A Widespread Phenomenon in Pharmacological Therapies