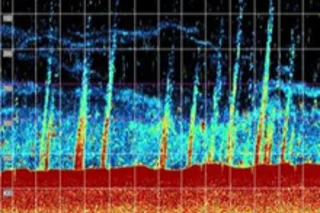
At the bottom of the Arctic Sea lie vast deposits of methane gas trapped in frozen, icy forms called methane hydrates, and climate scientists would very much prefer that it remains trapped down there. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas, and some researchers worry that a warming ocean may melt the icy structures, allowing the gas to travel up through the water to the atmosphere, where it could further contribute to global warming. Now, scientists who have been scanning the seas for signs of trouble say they may have found some. The researchers spotted 250 plumes of methane gas bubbling up through the sea north of Norway.
The region where the team found the plumes is being warmed by the West Spitsbergen current, which has warmed by 1 °C over the past 30 years. "Hydrates are stable only within a particular range of temperatures," says [study coauthor Tim] Minshull. "So ...