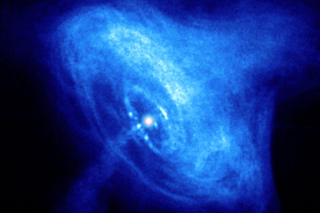
Astronomers using the Tibet AS-gamma Experiment have discovered the highest-energy light ever measured from an astrophysical source. Photons streaming from the Crab Nebula were recently measured at energies well over 100 tera-electronvolts (TeV). That’s a trillion electron volts, or some 10 times the maximum energy that the Large Hadron Collider sees when it slams particles together.
Scientists think the key is a pulsar lurking deep inside the heart of the Crab Nebula, the dense, rapidly spinning core left when a star exploded in a supernova almost a thousand years ago. Actually, since the nebula is located over 6,500 light-years away, the explosion occurred about 7,500 years ago, but the light from that explosion didn’t reach Earth until 1054 CE, when it exploded in our night skies as a bright new star, spotted by astronomers around the globe.
The supernova’s light faded after just weeks, but since then, the detritus has ...