Mining is low on the list of enviable occupations. The hazards one faces when plying one of humanity’s most ancient professions, burrowing deep into the earth to harvest its hidden treasures in the form of precious stones and metals, range from grungy to downright gruesome. The occupation is widely considered to be one of the world’s most dangerous, and it was only in the 1950s that the mining industry in the United States finally saw fatalities due to accidents dip under a thousand a year (1).
Not only do miners experience significantly increased morbidity due to working conditions that are inherently more challenging and dangerous than those posed by a corporate 9-to-5, but they also face a greater incidence of infectious diseases than your average desk jockey. Skin and respiratory illnesses abound in mines, tropical parasites such as malaria and dengue can plague those in more tropical locales, and rodents in infested mines can spread leptospirosis and other diseases (2). While these illnesses are still common in mines located in developing countries, the United States and the developed world have largely eradicated these ailments, leaving only the dark and dampness to do battle with.

Image: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
Image: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
With regard to disease, we often associate mining with tuberculosis and black lung, though there was one unexpected hazard that constituted a significant burden throughout the history of mining and onwards into the early 1900s: the bloodsucking hookworm.
Ancylostoma duodenale has a very particular geographical distribution; it’s picky about the temperature, humidity and type of soil that its eggs and larva inhabit. But in underground mines, the high levels of dissolved mineral salts in the loamy soil encourage parasitic growth. The worms flourish in the dank humidity and suffocating warmth that dramatically appear the farther one descends from the surface. Their life cycle is further enhanced if humans do not follow basic rules of sanitation and go barefoot.
The hookworm has a distinctly icky cycle of transmission: humans shed the larvae in feces, which, after a short period of growth and maturation, go on to penetrate the unshod feet of other unsuspecting humans. The larvae travel through thick soles and skin, through arteries and veins to the well-vascularized lungs, ascending up the throat, and eventually – finally! – emerging into the throat before being swallowed and delivered to the bowels. Their journey ends in the small intestine where they mature into their adult form and attach to the bowel walls to feed on blood, which can leave their hosts anemic.
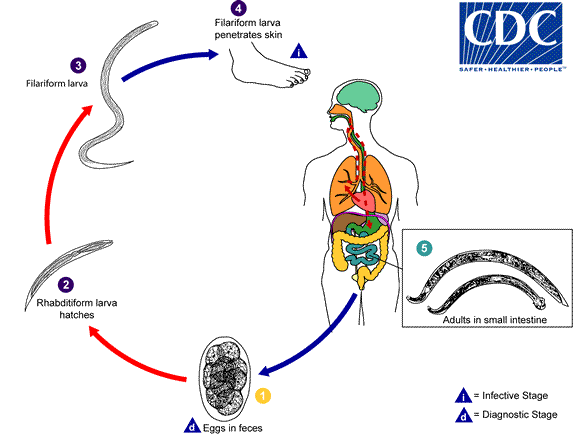
The life cycle of the hookworm. Image: CDC. Click for source.
Unfortunately, historical accounts indicate that defecating willy-nilly in the mines was a widely accepted practice up to the twentieth century. The hours miners worked were long, and ascending to the surface to attend to one’s business meant time away from work, time that was not likely to be granted to workers laboring without the protection of OSHA or similar agencies. Toilets in the depths were crude and few. A common practice was for stools to be laid among drain gutters, but an influx of rain from the surface would easily ruin these not-so-carefully laid plans, resulting in a literal shitschturm.
Even in mining operations that generously provided their men with the luxury of not having to defecate directly in their workplace, contamination was common, as one author describes: “Miners were in many instances expected to return to the surface to defecate when necessary, the usual result was that the men for sake of convenience and to avoid discomfort would almost invariable resort to abandoned or unfrequented parts of the workings”(3). Feces containing the hookworm larvae would be squished and squelched everywhere: throughout the mine and on ladder rungs, with infected men inadvertently spreading a worm and its disease onto his colleagues. For miners going barefoot or wearing improper footwear, the risk of hookworm infection was further increased.
Widespread hookworm infections among miners led to some of the classical stereotypes we associate with this occupation: pale men hacking and coughing from lung diseases, in some part due to the breathlessness and anemia caused by the staggering iron deficiency that accompanies infection by these bloodsucking parasites. In fact, “miners’ anemia” has been the nickname for Ancylostoma infection for centuries, along with other monikers such as “ tunnel disease,” “miners’ itch,” and “brickmaker’s anemia.” For centuries, it was thought that the anemia was intrinsically related to the occupation of mining, to the constant sun deprivation and coal exposure. It would only be in the mid to late 1800s, as the hookworm’s method of transmission was fully elucidated, that anemia would be finally attributed to a worm thriving in loamy soil, living high off of exceedingly poor sanitation.
The extent of hookworm infection was properly assessed in the mid to late 1800s. The disease was recorded throughout the United States, Australia and and much of Europe (4). It was found in the gold and silver mines of Hungary, Sicily’s sulphur mines, and in the coal mines littering Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France (5). It was estimated that 20 to 90% of miners in Austria suffered from anemia in the late 1800s. More than half of the men slaving away in the goldmines in the California Gold Rush in the mid-nineteenth century were thought to carry hookworm, with some populations said to be infected at a rate as high as 80%. In 1916, when the California State Board of Health investigated the prevalence of hookworm among the 1400 miners based at the Grass Valley Gold Mining district in Sierra Nevada, all but two of the men were found to be harboring worms (1).
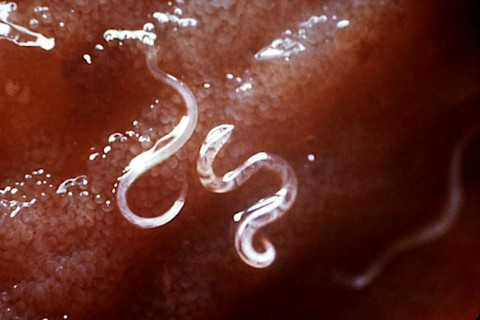
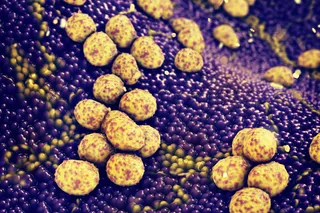
Two hookworms of the Ancylostoma genus attached to the intestinal mucosa. Image: CDC
Hookworm was the source of a “violent epidemic” outbreak of diarrhea and anemia among men constructing the Swiss Saint Gotthard Tunnel in 18803 (5). Hundreds were infected, and several died of overwhelming anemia. Physicians investigating the outbreak were “inclined to hold the adverse hygienic conditions responsible for the bad health of the men,” finding that miners were forced to defecate inside the tunnel during the workday and many, coincidentally, were wearing “leaky and wet” shoes (5).
One physician writing on the prevalence of the hookworm menace in Californian miners speculated that hookworm infection had been within the mining community for centuries, from the slave mines of ancient Egypt to the iron mines of medieval Europe and the modern operations of the Americans, endlessly cycling through millions of men sent into the dark mines for tin, coal, and gold (3). It was only until the early to mid 1900s, as both sanitary measures and efficient worm-killing drugs were introduced to miners that hookworm was banished from the mines.
Hookworm was, in short, an industrial, occupational disease. Though mining is a job fraught with danger and the threat of death, this lowly worm has been a surprising long-time companion. For centuries the proper sanitation of mines was but an afterthought compared to the threat of rock falls, explosions, flooding, and collapse. For this reason, hookworm was able to capitalize on a key pair of sanitary oversights common to pre-twentieth century mining: a culture of laissez-faire defecation and poorly clad feet. Thus, for generations of men working our mines, having a touch of hookworm infection was as common a plight as a slight cough or stepping in something decidedly untoward on their way to work.
References
1) United States Department of Labor. “Injury Trends in Mining.” Accessed on October 31, 2014 at http://www.msha.gov/mshainfo/factsheets/mshafct2.htm
2) AM Donoghue (2004) Occupational health hazards in mining: an overview. Occupational Medicine 54: 283–289
3) RW Nauss (1921) Hookworm in California Gold Mines. Am J Public Health (N Y). 11(5): 439-51
4) WA Sawyer (1923) Hookworm disease as related to industry in Australia. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine, 111(3): 159-176
5) Rockefeller Foundation (1922) Bibliography of Hookworm Disease. New York City, NY: The Rockefeller Foundation, International Health Board