A team from Rockefeller University in New York has provided the first good look at a crucial, if obscurely named, biological switch called the voltage-gated potassium ion channel. Nerve and muscle cells communicate by shuttling charged atoms through vast numbers of these tiny channels in their membranes. Without this system, you could not think a thought or lift a finger—and if the channels malfunction, the results can be disastrous.
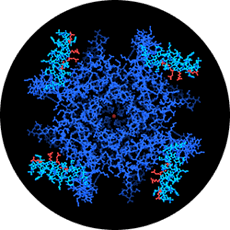
Photograph courtesy of Roderick MacKinnon/Rockefeller University.
Biophysicist Roderick MacKinnon and his colleagues started by crystallizing the proteins that make up the ion channel and bombarding them with X rays to reveal their structure. The results showed that the channel consists of a central pore surrounded by four paddle-shaped structures (see above) that can swing from the inside to the outside of the cell's membrane. The movement of the paddles allows the channel to open or close in response to voltage changes that occur when a molecular signal is sent. Fred Sigworth, a molecular physiologist at Yale University, is contemplating the practical implications. Voltage-switching problems contribute to many diseases, including diabetes, epilepsy, and heart arrhythmia, he says. "Now one can begin to imagine new approaches to the design of drugs that target ion channels."