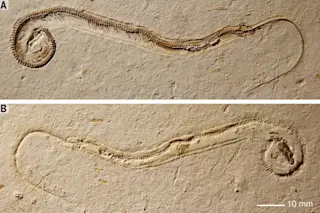
Snakes, with their sleek, slithering shape, are unmistakable amongst the reptiles. Yet for decades, scientists have been debating just how these limbless lizard relatives ended up with their distinctive, elongated body.
On one side are scientists who argue that the serpentine shape was an aquatic adaptation. Many snake traits, including an elongated body and reduced limbs, are also features of swimming animals (think whales and dolphins, for example, which have lost their hind limbs). Early evidence also suggested that snakes were closely related to mosasaurs, the terrifying and extinct group of lizards that were woven into pop culture the moment one was fed a great white shark in Jurassic World. Non-theatrically, these marine reptiles ruled the seas during the Cretaceous, and possessed many snake-y features, including a jaw which stretches for large prey. The discovery of extinct marine snakes with hindlimbs, including Pachyrhachis, Haasiophis, and Eupodophis, seemed further proof of ...